![[IUCr Home Page]](/iucr-top/logos/iucrhome.gif)
![[JAC]](/iucr-top/logos/j.gif)
![[JAC Indexes]](/iucr-top/logos/jc.gif)

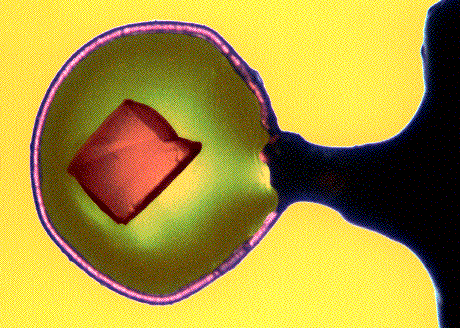
Cover illustration: A crystal of the protein phosphorylase b flash-cooled to 100 K in a 1 mm-diameter mohair loop prior to collection of X-ray diffraction data. Courtesy of Elspeth Garman and Stephen Lee, University of Oxford.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 889 - 892
Synopsis
A correction is shown for the Compton scattering intensity that is calculated theoretically for free atoms, if the loosely bound outer electrons of the atoms construct the conduction or valence band in crystals, typically in the case of aluminium and silicon.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 893 - 899
Synopsis
Atomic displacement parameters were derived from a temperature-factor analysis of Bragg reflections. An interpretation is given towards the migration of the oxygen ions under the action of an applied direct-current electric field.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 900 - 904
Synopsis
The design and performance of the new SAXS modular instrument having easily variable wavelength are described. Tests reveal a previously unrecognized phenomenon, namely diffuse scattering from the mirrors; this can be reduced by rearrangement of the positions of the slits.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 905 - 908
Synopsis
A novel angular-dispersive X-ray reflectometer that allows the measurement of the X-ray reflectivity of thin layers, contained in a chamber, is described. The X-rays are focused by a Johansson monochromator using the Si(333) Bragg diffraction.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 909 - 913
Synopsis
The crystal structure of a layered compound containing 24 independent atoms was solved ab initio from X-ray laboratory powder data. The procedures applied are described. By powder diffraction study, the appropriate chemical formula was found.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 914 - 917
Synopsis
Anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering measurements on the precipitation structure in an NiCrAl alloy have been performed. Ni partition was found to be the same in the matrix and the precipitates.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 918 - 920
Synopsis
The effects of heat treatment on the structure of flame-fused silica glass from amorphous and crystalline powders were investigated by small-angle X-ray scattering.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 921 - 931
Synopsis
A variant of the Rietveld refinement procedure applied to the characterization by WAXS of disordered and small crystals as found in semi-crystalline polymers is described.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 932 - 942
Synopsis
The radiation transmission characteristics of a tapered cylinder may be described using analytical expressions developed for the straight cylinder, but with a lower effective critical angle that depends on the taper length and angle.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 943 - 947
Synopsis
Off-specular neutron reflection from an optical grating has detected in-plane periodicity up to 42 micrometres. This is much longer than expected from the coherence length of the neutron beam but is consistent with the instrumental resolution.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 948 - 956
Synopsis
Scattering of colloids is identified by variation of the X-ray energy near the absorption edge of gold. Results from small-angle X-ray scattering after correction for absorption and refraction are compared with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and optical UV visible spectroscopy.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 957 - 962
Synopsis
A high-resolution structural study of magnesium formate dihydrate was performed using high-energy synchrotron radiation and an X-ray image intensifier/CCD detector.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 963 - 967
Synopsis
A cumulant expansion was performed to calculate X-ray or neutron reflectivity.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 968 - 974
Synopsis
A new development of the Monte Carlo technique for structure solution from powder diffraction data, involving restrained relaxation of the geometry of the structural fragment during the Monte Carlo calculation, is reported.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 975 - 984
Synopsis
A method for obtaining anisotropic correlation functions is presented and modelling of the scattering data by a modified paracrystal model is described.
See also Erratum: J. Appl. Cryst. (1996). 31, 490.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 985 - 995
Synopsis
The FOCUS method, in which both crystal chemical information and powder diffraction data are included in the structure determination process, is presented. FOCUS combines automatic Fourier recycling with a specialized topology search specific to zeolites.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 996 - 1001
Synopsis
This paper describes an algorithm for peak search in the three-dimensional Fourier map that is more convenient and faster than conventional two-dimensional Fourier synthesis.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1002 - 1007
Synopsis
A novel method of analyzing X-ray peak broadening due to mosaicity for double-crystal X-ray diffraction measurements is proposed.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1008 - 1015
Synopsis
The peak profiles of standard reference materials have been investigated with energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction at a synchrotron source. A single-line profile analysis was performed to obtain estimates of size and strain in plastically deformed f.c.c.-based metals.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1016 - 1021
Synopsis
Results from in situ grazing incidence diffraction and X-ray reflectivity measurements at different temperatures are presented. The structure, texture and epitaxic growth of thin Pt, Pt2Si and PtSi layers on Si(111) and (001) surfaces are analyzed.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1022 - 1025
Synopsis
An automated program for molecular replacement using a full-symmetry translation function combined with a packing function is described.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1026 - 1035
Synopsis
The oscillatory deviations arising from parallel interfaces, when the latter are diffuse, are still observable in the Porod plot provided that the ratio of the diffuse region thickness to the parallel interface distance is less than 1/4.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1036 - 1040
Synopsis
A fast and reliable algorithm has been developed for autoindexing oscillation images. The program has successfully determined the lengths and directions of basis vectors for numerous unit cells having cell dimensions ranging from 16 to 688 Å and oscillation ranges from 0.2 to 2.0 degrees.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1041 - 1047
Synopsis
Properties of the decomposition kinetics in Cu-Co alloys were determined by time-resolved ASAXS measurements.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1048 - 1055
Synopsis
The treatment and analysis of SAXS data are reviewed with specific concern for glass science. The methods developed are illustrated by SAXS and ASAXS scattering results obtained from optical filter glass, glass produced by the sol-gel technique, optical colourless glass inclining to opalescence, porous glass and single-phase phosphate glass.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1056 - 1064
Synopsis
The primary phase formation in an MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 base glass for glass ceramics was investigated by combining different small-angle scattering techniques. The effect of TiO2 and ZrO2 as nucleating agents on the first stage of crystallization was clarified using contrast variation.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1065 - 1074
Synopsis
Small-angle X-ray scattering was used to characterize various mesoporous silicas, aluminosilicates and gallosilicates.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1075 - 1083
Synopsis
Liquid-crystalline halato(semi)telechelic polymers have been studied using small-angle X-ray scattering and small-angle neutron scattering
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1084 - 1095
Synopsis
The development of structure and morphology during the heat-draw process of a nylon 66 fiber was investigated by two-dimensional WAXD and SAXS methods using synchrotron radiation. The results indicate that a premelting process precedes the Brill transition during the chosen processes.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1096 - 1104
Synopsis
Glancing-angle neutron diffraction has been used to study the variation in smectic layer tilt in high- and low-pretilt smectic C cells with distance from the surface.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1105 - 1111
Synopsis
Time-resolved small-angle light scattering was used to study phase separation phenomena of the water-octane-tetraethylene glycol monodecyl ether microemulsion system.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1112 - 1124
Synopsis
Structural parameters of biopolymers derived from small-angle scattering were used to calculate and estimate hydrodynamic parameters. The validity of several approaches was tested with different types of molecules.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1125 - 1131
Synopsis
Questions of biological structure research that cannot be solved because of insufficient contrast conditions could be answered by spin contrast variation.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1132 - 1139
Synopsis
A numerical approach to the evaluation of two-dimensional small-angle neutron scattering data which includes interparticle-interference and multiple-scattering effects is described.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1140 - 1147
Synopsis
The present and future prospects of small-angle neutron scattering at pulsed neutron sources are reviewed.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1148 - 1149
Synopsis
The antiphase domains can be explained in terms of the ordering of the Cl ion in the channels of the chlorapatite structure. The displacement vector of the domain was found to be (1/2)[010].
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1150 - 1151
Synopsis
Experimental observations of the fine structure of a bent-crystal rocking curve, made with a double-crystal diffractometer, are reported.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1152 - 1155
Synopsis
X-ray powder diffraction on mixed crystalline samples has been performed to determine which of the two forms of l,2,4,5-tetrabromobenzene (TeBB) is isomorphous with the room temperature form of l,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene (TeCB). It is found that beta TeCB is isomorphous in the strictest sense (i.e. capable of giving a continuous series of mixed crystals) with the gamma form of TeBB.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1156 - 1158
Synopsis
An X-ray powder diffraction study of the structural characteristics and thermal expansion between room temperature and 873 K is reported for the system HoNi5-xAlx, 4 >= x >= 0.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1159
Synopsis
Correction to J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 495 - 501.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1159
Synopsis
Correction to J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 487 - 494.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1160 - 1161
Synopsis
The program ALIGN determines the transformation to superimpose structurally homologous protein domains. The results are expressed in terms of the rotation and translation necessary to effect the transformation.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1162 - 1164
Synopsis
A new single-crystal mounting technique for high-temperature X-ray diffraction up to 1700 K is briefly described. The major advantage of the method is the very low background, because the sample is clamped by thin microcrystalline fibres without using any glue or cement.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1165 - 1166
Synopsis
A helium beam path for the marresearch imaging-plate detector system is described.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1167 - 1172
Synopsis
A periodic nodal surface that partitions a unit cell into regions of high and low electron density can be calculated from a few strong, low-index reflections. This `structure envelope' can then be used to facilitate structure solution from powder diffraction data.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1173
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1173
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1173 - 1175
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1175
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1176
J. Appl. Cryst. (1997). 30, 1182
Copyright © 1998 International Union of Crystallography
IUCr Webmaster